Fast charging is one of the most important features of mobile phones in 2021. Let’s see how it works, the different types that exist, and what are their pros and cons.
10 years ago the mobile battery lasted a day and now it continues to last more or less… a day. It seems that we have not advanced at all, but it is the opposite. Now smartphones are 100 times more powerful than a decade ago. So we have batteries 100 times more powerful, with an exceptional charge density, and an impressive energy capacity, for what little they occupy.
The problem is that users do not care about the cutting-edge technology behind a battery. The only thing that matters is that it recharges as soon as possible. That is why fast charging has become one of the most important aspects of modern mobiles.
There are many types of fast charging (in practice, each brand uses its own), with different performance, so let’s see how they work, how to know if a mobile supports fast charging or not, and what are the advantages and disadvantages.
Although manufacturers do not talk much about it, fast charging has a price, and it is important to take it into account, as we will see.

All about fast charging on mobiles..
What is fast charging?

A fast-charging mobile is telling us that the battery can recharge faster than normal. It has no more mystery. If a certain mobile takes 2 hours to recharge with a standard recharge, using fast charging will take less time. It can be 1 hour and a half, or even 1 hour. Today there are already fast-charging mobiles that recharge in less than 30 minutes.
The problem is that there is no single type of fast charge. There are many different ones, and even within the same type, there are different loading speeds. Therefore, before explaining how fast charging works, it is convenient to know some basic concepts of mobile batteries.
This is how a battery works

We are going to try to be brief and use simple terms, but if this section seems too technical you can skip to the next one, although it is worth understanding.
A battery is actually a container that contains chemical components (nickel-zinc, lithium, etc.) that react to the passage of electrons. Batteries have a positive pole, the anode, and a negative pole, the cathode.
When we turn on the mobile, these poles connect, closing an electrical circuit where electrons move. Those electrons react with the chemical components of the battery, generating an electrical current that is used to power the hardware of the mobile.
And how is the capacity of a battery measured? Three values are used: Amps (A), Volts (V), and Watts (W).
The amps indicate the intensity of the electric current, that is, if more or less electricity passes in a certain time.
That is why the capacity of a battery is measured in mAh, that is, milliamperes per hour. If a battery is 2,500 mAh, it can supply an electrical current of 2,500 milliamps in one hour.
The next important value is the battery voltage, which is measured in Volts (V), and indicates the electrical voltage.
Finally, we have the value that interests us the most: the battery’s charging capacity , that is, how much electrical intensity it can accept depending on the electrical voltage it uses. It is measured in Watts (W), and its calculation is as simple as multiplying the volts by the amps. W = V * A.
For example, a mobile with a voltage of 5V and a current intensity of 2A, has a load capacity of 5V * 2A = 10W.
We already know everything we need to master fast charging.
Understanding the charge of a mobile

Before discovering why fast charging is more efficient than normal charging, it is important to know how the mobile battery recharges.
We have already seen that a battery uses a certain current, measured in Amps, at a certain voltage, measured in Volts.
The problem with lithium-ion batteries , the most used by mobiles, is that they are very sensitive to high voltages, as XDA-Developers explains. When they receive a lot of volts they get very hot, and they suffer.
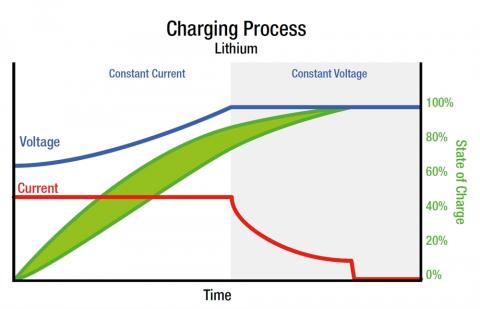
For this reason, when a battery is recharged, the voltage never rises above a certain value considered safe . At the same time, the current (the Amps) remains constant in the first part of the recharge, but then gradually drops until it reaches zero. In summary, recharging has three different phases, where the mobile recharges at different speeds. In this graph you will see it more clearly:
The important thing here is that the voltage and current vary during recharging , and that is what different fast-charging systems are going to play with to recharge faster.
How does fast charging work?
Although, as we have said, lithium-ion batteries do not accept very high voltages, fast-charge chargers still manage to use a high voltage, which accelerates charging. Instead of using 5V they go up to 9, 12, and even 20V. Mobile phones with support of this type of charge have internal circuits called buck converters, which convert high voltage into low voltage while maintaining the intensity of the current, and without generating much heat.
This allows you to recharge your mobile faster without damaging the battery. An attempt is made to charge the battery as quickly as possible during the first phase, before the current flow begins to decay. From that moment on, the load will be much slower.
That is why many manufacturers offer data such as: ” The mobile is recharged to 70% in 20 minutes“. What they don’t say is that the remaining 30% is much slower, and sometimes takes longer than the initial 70%.
The different types of fast charging that we are going to see use different types of circuits to regulate the voltage and current, and different algorithms that adjust the charging phases according to the characteristics of the mobile, that is why most brands use their own system.
From what values is considered fast charge?
The charging of a mobile is carried out through a USB connector. Therefore the normal load will give us the capacity of that connector. Smartphones use micro-USB and USB Type-C connectors.
The micro-USB cables accept a current of 2A and a voltage of 5V. So its charging capacity is 2A * 5V = 10W.
The USB Type C Cable accept a 3A current and a voltage of 5V. So its load capacity is 2A * 5V = 15W.
So it’s very easy: any mobile with a micro-USB connector that recharges at more than 10W has fast charging. If it is a mobile with USB Type C, the fast charge begins beyond 15W.
For example, a simple fast charge is 18W, which uses 2A and 9V, that is: 2 * 9 = 18W. A faster version, at 40W, is achieved using 4A and 10V, with which we obtain: 4 * 10 = 40W.
These are values that are outside the standards, so fast charging requires its own charger, and its own cable. If you use a different one, it will not reach those values.
As for wireless fast charging, the theory is the same, as it works the same. The only difference is how it transmits the electricity, through the air instead of a wire, but once power reaches the battery, the operation of the recharge is the same. Of course, wireless charging is usually slower.
How can I know if my mobile supports fast charging?
In modern versions of Android or iOS, when the mobile is using fast charging, a message or a special icon appears indicating this.
In Settings, in the Battery section, some mobile brands also indicate this.
Another option is to look at the sticker on the charger. You only need the Amps and Volts. If the sticker says 2A / 5V that is 10W, which, as we have seen, is not fast charging. But if you put 2A / 9V, it’s 18W, which is already fast charging (although one of the slowest).
This brings us to an important point, and that is that fast charging depends on the charger. Your mobile may be compatible but if you use a lifelong charger, it will use the normal charge.
Other sites where you can see this information is in the mobile manual, or on the manufacturer’s website.
Advantages and disadvantages
We have already seen the main advantage of fast charging: its speed. They can reduce the recharge time of a mobile up to 70%.
The theory tells us that the battery does not suffer more than necessary to charge quickly, because mobile phones use circuits and algorithms that slow down the charge when the battery gets too hot, or reaches a certain voltage.
But it is also true that marketing plays an important role here. There is a race to see who charges the mobile the fastest, and this causes the security algorithms to be stretched to the maximum.
Fast charging is safe, and if you have it, it’s worth using. But some reviews say it could deteriorate the battery in the long run. So our advice is that you only use it when you need it, especially in summer. And especially, do not use it at night. If you are not in a hurry to recharge or are going to do it while you sleep, better use a normal charger.
We also advise against recharging the mobile while it is being used.
Quick charge types
There are a handful of types of fast charging, as we are going to see, depending on the voltage and current they use, and their methods of recharging.
Almost all of them are based on the two generic platforms: USB Power Delivery , which offers the USB standard, and Quick Charge from Qualcomm. Brands take these standards and modify them according to the characteristics of their mobiles.
USB Power Delivery (USB-PD)

The USB format itself, which is used by all mobiles through the micro USB and USB Type-C connectors, also offers an option to use fast charging.
The first generation was released in 2012, and allowed a power of 60W (3A and 20V) through micro USB.
The second generation, via USB TYPE C, is more versatile. It allows to use voltages between 5V and 20V for a maximum power of 100W. Although in practice in mobiles it only allows up to 45W.
A third generation with PPS technology, launched in 2017, allows you to use precise increases in amperage and voltage, to obtain very precise charge capacity, depending on the battery.
Qualcomm Quick Charge
Qualcomm offers a fast charging standard for all brands using its Snapdragon processors. For a few years it was the most used system, but now each brand uses its own, although most are based on Quick Charge itself.
Quick Charge 1.0 was launched in 2013, and it offered a charging capacity of 10W (2A and 5V), which today is considered the limit of normal charging.
Quick Charge 2.0 increased the voltage to 12V. Thus, loads of up to 24W are achieved with micro USB, and 36W (3A and 12V) with USB Type C.
Quick Charge 3.0 was released in 2015. Its main contribution is that it allows you to use voltages during recharging in increments of only 0.2V. But it still maintains a capacity of 36W.
Quick Charge 4.0 and 4.0+ focused on improving the safety of charges, to reduce heating. They reach powers of 100W.
Finally, in 2020 Quick Charge 5.0 was released, with charging capacities of more than 100W, recharges up to 50% in 5 minutes, and a decrease in battery heating by no less than 10 degrees Celsius. It is also capable of generating two electrical currents to charge two cells at the same time, in batteries that use more than one.
One of the advantages of this platform is that its chargers are compatible with all the previous standards. In other words, a QuckCharge 5.0 charger can charge a 1.0 mobile, but at the speed of QuickCharge 1.0. Although there are some exceptions, which you can see in this table:
Be careful because Quick Charge not only works with Android. It also does it with iOS. But only as of Quick Charger 4.0.
Xiaomi Super Charge Turbo
Xiaomi uses Qualcomm’s Quick Charge technology, although it has its own name: Super Charge Turbo, which it introduced in 2019.
Xiaomi Mi 10 Ultra was the first mobile to fully exploit Quick Charge 5.0, to reach an incredible 120W. However, the new Xiaomi Mi 11 takes things slower and stays at 55W for wired charging, and 50W for wireless charging.
Huawei and Honor SuperCharge
Unlike previous technologies, Huawei uses a recharging system that is not based on increasing the voltage, but the current (Amps).
The first version, presented in 2017, reached a capacity of 22.5W (5V and 4.5A). The P30 and P40 range, as well as Mate 30 and Mate 40, go up to 40W.
The Huawei Mate 40 Pro holds the brand’s record with a load capacity of 66W (11V and 5A), but it could be surpassed by the Huawei P50 which will be presented shortly.
Samsung Super Fast Charging
Unlike Chinese companies, which compete to see who offers the most powerful recharge, Samsung has always been more restrained in this regard. We all remember what happened to the exploding batteries in the Galaxy Note, and you don’t want it to happen again.
Its system is called Super Fast Charging and it is based on USB-PD PPS, so it is compatible with generic fast charging chargers.
The 2019 version ran at 25W (11V and 2.25A), but with the Galaxy S20 range it released Super Fast Charging 2.0, which reached 45W.
However, with the new S21 range released this year it has dropped to 25W in cable charging, and 15W in wireless charging, as in the Samsung Galaxy S21 Ultra 5G.
Apple USB-PD PPS
As with Samsung, fast charging is not a priority for Tim Cook’s company .
It started using it in 2017 and it conforms to the USB-PD PPS standard, so it is compatible with third-party fast-charging chargers. In fact, you will have to buy it yourself, because Apple no longer includes a charger with its mobiles.
From the iPhone 8 to the iPhone 10 it used fast charging at 18W, but from the iPhone 11 Pro Max it uses fast charging at 27W in its most powerful models, such as the iPhone 12 Pro Max.
OPPO, Realme, Vivo and OnePlus
Oppo is already the brand that sells the most mobiles in China, surpassing Huawei and Xiaomi. It is part of the BBK group, which also owns other brands such as Vivo, OnePlus or realme. They all use the same fast-charging technology, as XDA Developers discovered , so we have grouped them together. But for marketing reasons they have different names.
The pioneer was Oppo, which in 2014 released VOOC, which works almost the opposite of the competition. Instead of increasing the voltage too much, the current increases. Thus he managed to reach 20W (5V and 4A) with VOOC 2.0. Realme used it with the name Dart, and OnePlus with Dash.
In 2016 Super VOOC arrived , reaching 50W . It was intended for the premium range, so in parallel it developed VOOC 3.0 with 25W more modest performance and VOOC 4.0 , which reached 30W (5V and 6A). It is also used by Realme and OnePlus on their mobiles from 2 years ago,
The most advanced version is Super VOOC 2.0, which reaches 65W (10C and 6.5A). It is also used by Realme with the name of SuperDart and OnePlus, with Warp. We can find it in mobiles such as the Realme X50 Pro or the recently presented Oppo Find X3 Pro, capable of recharging the battery to 100% in 38 minutes.
The wireless variant is called AirVOOC , and it currently reaches 30W .
Oppo has also introduced the fastest charging in the world, at 125W , using GaN chargers , capable of recharging a 4,000 mAh battery in 20 minutes. But it is still in the development phase.
Realme is also working with this 125W fast charge that it calls UltraDart. It is based on using different layers of thermal insulation to reduce and expel heat, and is capable of charging a mobile to 33% in 3 minutes, and 100% in 20 minutes. Impressive!
MediaTek Pump Express
Mobiles with MediaTek processors use the Pump Express fast charge, launched in 2013. A year later, Pump Express + debuted, with a charging capacity of up to 24W.
The most modern version is Pump Express 4.0, reaching 75% charge in 30 minutes. It is also compatible with USB-PD 3.0, and with wireless charging (up to 15W).
Motorola TurboPower
Finally, we have to talk about Motorola’s TurboPower charging , which, although it is based on Qualcomm’s Quick Charge, uses its own heat dissipation technology and voltage management algorithms.
Motorola mobiles are compatible with Quick Chage 2.0 and 3.0 and the models of the last two years work with loads at 18 and 27W. You need your own chargers.
We have seen what fast charging is and the different most important types that exist . We hope the information has been useful!
