The interest in the words Deep Web is surprising. The fact of thinking about a hidden Internet full of mysteries uncovers the curiosity of anyone, but the truth is that there are many false myths and anyone can access the Deep Web / Dark Web (or any of the other darknets) in a simple way. In this article we solve everything related to the Deep Web, what it is, differences with other darknets, myths and truths and finally, how to enter the Deep Web.
If you are here it is because you browse the Internet, obviously, because Technoeager only exists online. And surely you know WhatsApp, Facebook, Google and a long etcetera. But did you know that ‘underneath’ all that is another part of the Internet? You only access a part if you use Chrome, Firefox, Safari or similar. But some of what exists on the Internet is hidden from you, and a part of it is accessible only with special web browsers. We tell you what the Deep web is, how to enter, how it differs from the Dark web and what links to start with.
What is the deep web
The Deep Web is also called as ‘deep Internet’. And it is so named for the simple reason that it is made up of all Internet content that, for various reasons, is not indexed by search engines such as Bing, Yahoo or Google itself –among many others-. What all users use on a daily basis, however, is called the ‘surface Internet’.
The birth of the Deep Web is not mysterious at all. The truth is that everything is due to the arrival of a search engine, such as Google, Yahoo or Bing) that index much of the information on the Internet. In fact, if these browsers indexed more pages, the “deep internet” would shrink.
In addition, there are private websites that belong to the Deep Web without many knowing it. For example, the private area of a company, the user area of an operator or the private website of a university, have information that is not indexed in any search engine. However, everyone attributes the term Deep Web to illegal things and the truth is that all unindexed content falls into the category.
Deep Web vs Dark Web vs Darknet vs Clearnet
The concept of Deep Web should be used to define all web pages that are not indexed by traditional search engines. However, the term Dark Net is also often used to refer to the illegal, dark and not recommended part. The reality is that with the Dark Web or dark Internet, we should refer to the different darknets, networks that overlap the public Internet and require specific software and configurations or authorization to access.
We all know Tor as one of the darknets, but the truth is that there are others like Freenet or I2P with very valuable resources. It can be said that the dark web is a collection of networks and technologies used to share information and digital content. They use “non-standard” protocols and ports on the underlying network. The definition varies according to the authors, since others believe that they must also hide the very identity of the members of the network.
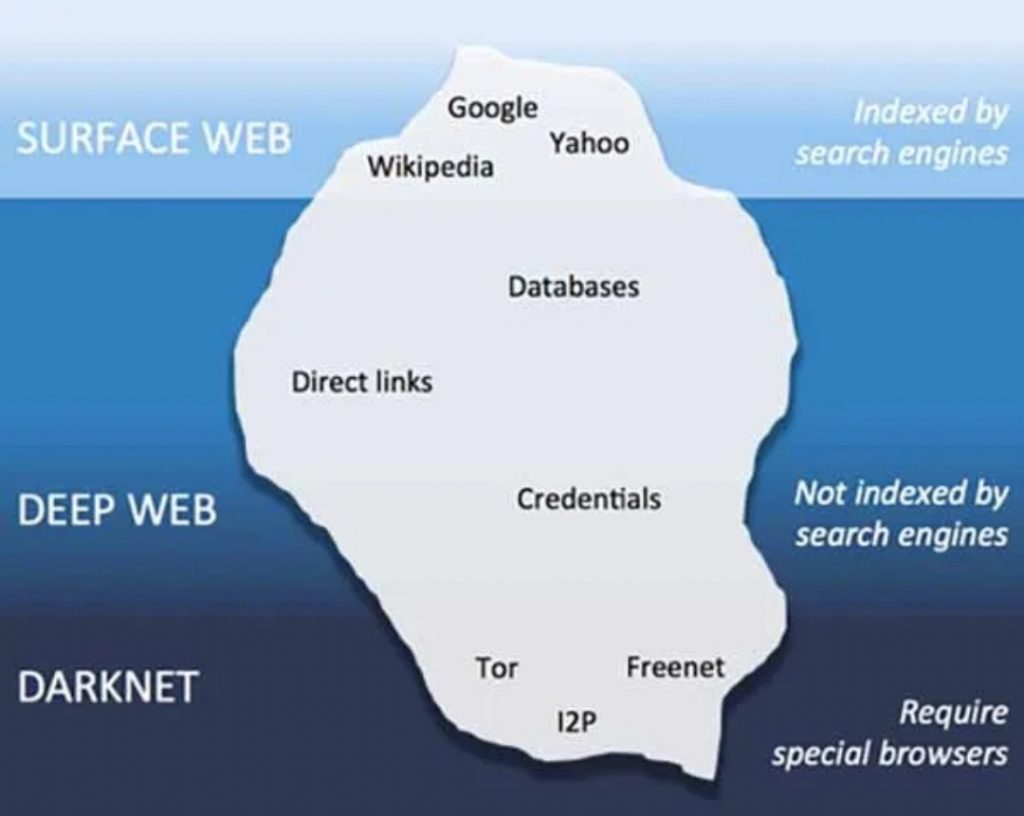
The Freenet, i2p, GNUnet, Entropy, ANts P2P, and Tor networks can be given as an example of Darknet networks, so we should not just stick with Tor as the maximum exponent of the Deep Web or Dark Web. We have two types, the P2P or peer-to-peer ones like Freenet, i2p, GNUnet, Entropy, ANts P2P and the non-P2P ones like Tor. The former stand out for their anonymity compared to the latter.
Why the Deep Web is ‘Hidden’
For practically any content on the deep web (Tor), what are used are domains with the .onion extension; furthermore, the domain names themselves are encoded with a HASH frame. There is no registration of these domains by a DNS server, but the .onion domains, with a specific service, are in charge of acting as this DNS. In a P2P network, the databases corresponding to the resolution of the HASH domain names are replicated so that they are available to all users. Instead of using the UDP / IP protocol for the identification of web pages, as in the superficial Internet, in the deep web they are repeated by a branch.
Although it is popularly believed that the deep web is dangerous or illegal, it hides technological and scientific advances, for example, in what is called the Academic Invisible Web. On the other hand, it is also believed that the deep web is ‘smaller’ than the superficial Internet, yet the latest estimates point to a dimension between 400 and 550 times larger than the surface Internet. Around 550 trillion individual documents, compared to 1 trillion on the surface Internet.
What’s on the Deep Web: Myths and Truths
In the Deep Web there is everything since, as we have explained, it is the unindexed part of the Internet. In addition, in each of the darknets, the contents can be very varied. When trying to place anonymity above all else, something that is not always achieved, they are often used for illegal activities, but we can also find a lot of academic work and research. In fact, this is known as Academic Invisible Web and encompasses databases that contain technological advances, scientific publications, and academic material in general that cannot be easily accessed.
The Deep Web also hides sites for the sale of drugs, fake money, false documentation, weapons, explosives, mercenaries, organs, hackers, personal information, classified books, pornography and other similar content. In addition, it is not very difficult to reach this content in a few minutes, although the level of confidence to buy, for example, counterfeit notes or false documents, leaves much to be desired.
Among the myths of the Deep Web we find those related to its size. Although some studies, such as the one we highlighted earlier, indicate that it is larger than the surface Internet, a recent one disproves it. The Recorded Future company confirms that the Dark Web is really tiny compared to the visible web that users and businesses use on a daily basis. Of the 55,828 different Onion domains, they saw that only 8,416 domains were active on the anonymous Tor network, making the percentage that the Dark Web represents 0.005% of the visible web, meaning negligible.
“Entering the Deep Web is illegal, you can go to jail” – False, browsing the Deep Web is not illegal, but certain actions on the Deep Web can lead to legal problems.
“In the Deep Web there are only drugs, weapons, child pornography…” – False, in the Deep Web there is content of all kinds, both products and services and documentation. We will not only access illegal products, services and documentation, but of all kinds.
We already have two fundamental aspects denied and, knowing what the Deep Web is not, what is it really? It is nothing more than a “parallel Internet” protected by traffic protection systems that are designed to maximize privacy and anonymity. Therefore, in the Deep Web we can find absolutely everything that we can imagine, and especially things that in the superficial Internet have no place.
How to enter the Deep Web
To access the deep web, as a broader concept and referring to TOR, a special web browser is enough. We can use Tor Browser, which is the most popular web browser in this field, but there are many alternatives to Tor Browser to access the deep web. Taking Tor Browser as a reference, what we would have to do to enter the deep web is the following:
With the newly installed web browser, we would have to open it and click on Open Settings to modify the corresponding parameters if, for example, our operator applies special restrictions, if we use a connection through a proxy server, or if we have configured on our computer – or on our network – a firewall. Then you just have to follow the guided configuration process in the web browser and, automatically, it will open as if it were Google Chrome itself or any of its similar ones.
Tor Browser is based on Firefox and can actually be used just like Mozilla’s web browser. That is, it serves us without any problem to navigate the superficial Internet. Now, if we want to access the Deep Web, then we should get the .onion links corresponding to the web page we want to visit. But as long as there is no search engine that has everything indexed in the same way as in the superficial Internet, we can always use the various mirrors of The Hidden Wiki, and other link directories on the deep web.
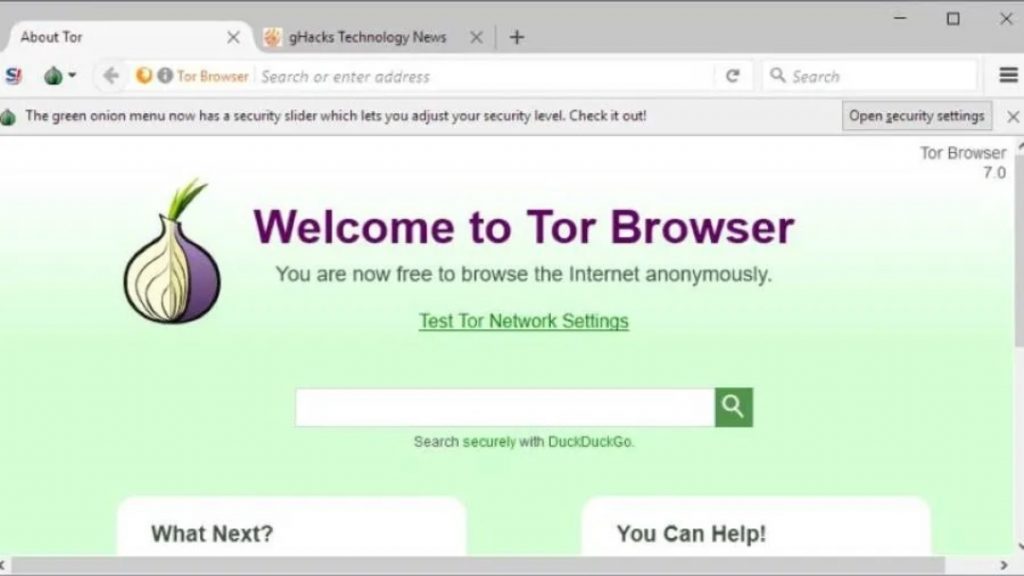
Furthermore, you can also download Tor Browser for Android from the official Google Play Store app store. The operation is similar to that of the desktop version. The versions for Windows and Android are not the only ones since on their official website they offer versions of the browser for macOS and Linux.
Tor Browser is the simplest alternative to access the Deep Web, but it is not the only one. To access other darknets, we can also use tools such as ZeroNet, Freenet and I2P, although we recommend them for more advanced users. The best thing is that you review our article on browsers for the deep web, where we explain you in great detail.
Searches on the Deep Web
As we have indicated previously, the Deep Web or Deep Web refers to all those sites that a common search engine, such as Google itself, cannot or does not want to index . In short, a specific place on the Internet that is distinguished by its anonymity and where many will wonder how the searches of these sites that are not indexed in the main search engines are carried out.
This is where the potential of the databases used in the deep web and the systems used to find the resources of the Deep Web on different Internet servers comes into play. In this way, it is possible to automatically detect resources that are not linked to the surface web.
Broadly speaking, Google’s deep web search system pre-calculates the submissions of each HTML form and adds the resulting pages to the Google search engine index. The results return thousands of queries per second to the content of the Deep Web using three key algorithms:
- The selection of input values : for inputs accept text search keywords.
- The identification of the inputs that allows accepting specific values such as the date.
- The selection of a small number of combinations that generate the appropriate URL to add in the search index.
When a search engine is accessed and a query is made, it does not search the entire Internet in search of the results, but only searches its own database. A database that has previously been generated and indexed and is known as a crawler.
Results displayed on the deep web are rarely displayed in conventional surface web search engines, as crawlers do not crawl or extract information from databases. In addition, they are not able to show password-protected pages or those that are not created in HTML language, although little by little some Deep Web search engines are incorporating other types of pages.
How to access other darknets
As we have said, Tor is not the only darket in the world and there are others that we can try, both out of curiosity and to find something we are looking for. Next, we tell you how to navigate through each of them.
ZeroNet
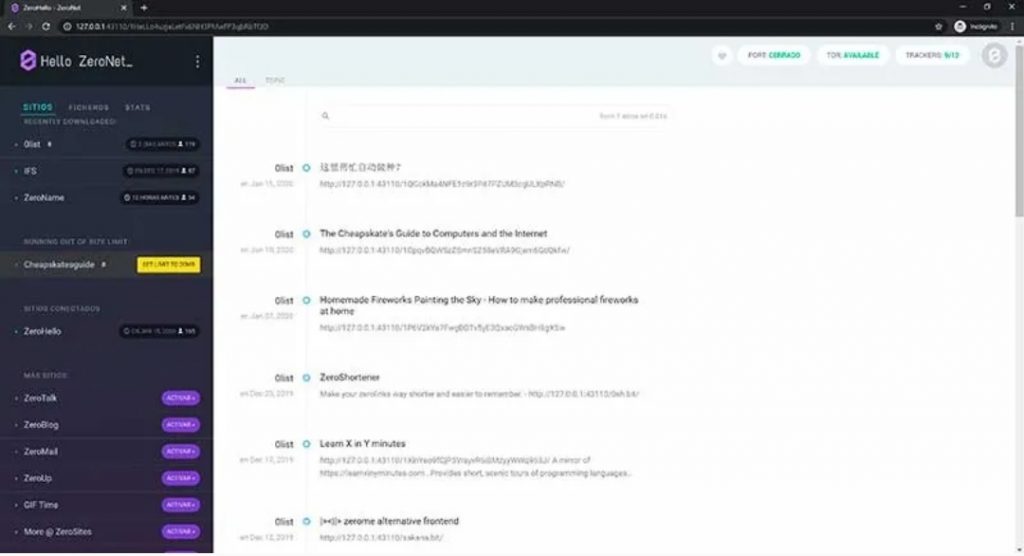
The first of the alternative darknets to Tor that we are going to know is ZeroNet, an open, free and uncensored network that uses Bitcoin cryptography and the BitTorrent network. We must be clear that the content is distributed directly to other visitors without any central server and that everything works with .bit domains.
To start with it, we must download the ZeroNet executable for Windows, macOS or Linux. In this case, we tell you step by step the process of use in Windows. Once we have the download on the PC, just unzip the contents of the .zip to run the ZeroNet.exe file.
This will open a new tab in our usual browser with an address that begins with http://127.0.0.1:43110/, we will also see the ZeroNet icon on the taskbar. A good place to get links is 0list to which users send the websites created within this Darknet.
Freenet
Freenet is free software that allows you to anonymously share, browse and post files pages, as well as chat and forget about censorship. It is a P2P or decentralized network that was born in 2000. All its nodes are encrypted and make it extremely difficult to identify the person demanding content. Users contribute to the network by giving bandwidth and a portion of their hard drive.
We will start by downloading the Freenet installer from its official website. We have this available for Windows, macOS and Linux. The installation process is very simple and, once finished, Freenet will open with our usual browser. In the case of Windows, the one at hand, we must have Windows XP or a more modern version. Freenet needs Java.
Once the installation process is finished we can run Freenet . Again, we will have an icon in the bottom bar indicating that we are connected to this network. The first time, we will have to define the security level we want to use (for the highest level we must have a “friend” on the network). In addition, we will have to answer some questions about our connection.
To begin with, we can do it through The Filtered Index, a directory with access to a lot of content. Every time we click on a link, the website in question will start to load and in a few seconds we should have access to it, although it all depends on our Internet connection. Other alternatives are to use Enzo’s Index, Nerdageddon or JFniki Index.
I2P
We finished the review of darknets with I2P. I2P is an anonymous network built on the Internet. It enables users to create and access content and create online communities in a dynamic, distributed network. Its goal is to protect communication and resist monitoring by third parties, such as ISPs.
Access also requires the installation of special software. I2P is available for Windows, macOS, Linux, and Android, requiring Java. The first step is to download I2P. After running the installer in Windows, we will simply click on the “Start I2P” button that will open the I2P router console, where we will find more instructions.
Now is the time to set the language and other things. In a very short time we will be on the I2P home page with access to various applications or web pages. We will have to wait a few minutes for I2P to start up and find other pairs to connect.
Links, links and sites for the Deep Web
The Hidden Wiki is the ‘starting point’ for browsing the dark web; but the original is practically unknown. So we can turn to deep web link directories that are similar and that, after all, fulfill exactly the same function. In fact, a version of the Hidden Wiki exists within the surface Internet, and indexed by Google. You have it in the following link:
From here we can find, as in The Hidden Wiki in its versions of the deep web, a directory of dark web links with different categories and sections. One of them for lists of hidden services and search engines, another for financial services, another for commercial services, markets for different substances, accommodation services, blogs, forums, instant messaging and communication services, politics…
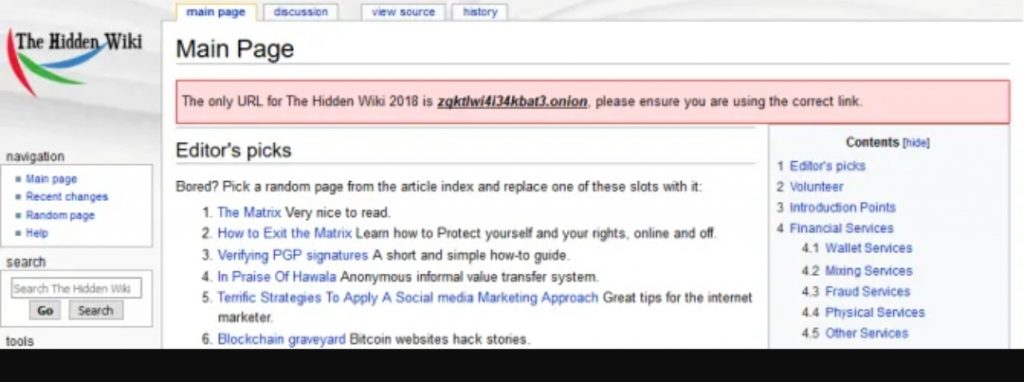
If we access this directory that we suggest from Tor Browser, then it is as simple as taking any of the links from the deep web, copying and pasting it in the address bar of the web browser, or clicking on it. The links of some of these online services change periodically so, although this directory is updated almost constantly, it is possible that some of them do not work. In addition, sometimes additional measures are necessary to protect the connection and traffic to access certain sites on the dark web.
Other deep web search engines
In addition to the previous one, we have a series of Deep Web search engines that will allow us to find the content we are looking for. Some of the most prominent are:
- torch
- Candle
- Tor Links
- NotEvil
- Grams
Don’t even think about entering the Deep Web if…
Would you let a child go online on their own for the first time? If you are a responsible parent or family member, the answer to this question should be negative. But is it dangerous to googling? If you know how to do it and you know what you are doing, no, but through Google all kinds of information, products and services are available that, in the hands of those who should not be, yes, it can be a significant danger. So far, everyone agrees, right? (If you do not agree, you can “scroll” to the end of the article and, in the comments section, delight us with your knowledge about pedagogy and training, about ethics… everything you can think of).
Exactly the same thing happens with the deep web, and before we start browsing it we should keep in mind that we are children in unknown terrain, so it is advisable to train before tackling the darkness of the Internet. And taking into account what we will find (with extreme ease) on the Deep Web, it is recommended that impulsive, morbid and inexperienced people abstain.
Frequent doubts about the Deep Web
- Why do the websites have such an old design ? Plugins, style sheets, and other “currents” of the surface Internet have not been adopted by the Deep Web simply because they are not needed. What is intended is free and anonymous browsing, not the massive traffic that rewards websites on the surface Internet with advertising and other monetization systems.
- Why does everything load so slow on the Deep Web? Tor Browser is a web browser based on Firefox, but with extensions and add-ons to avoid traffic tracking. Our traffic is “routed” to prevent tracking, which leads to longer load times, since connections to servers are indirect.
- Can I buy on the Deep Web? Yes, and on hundreds of web pages, but most require Bitcoins for this. On the Deep Web itself you will find guides on Bitcoins wallets and virtual currency purchase services.
- Why are some links not opening? The Deep Web is a whole world with different layers, some accessible only with advanced traffic protection systems, others with private invitation… Therefore, to access the entire Deep Web you will have to look for some more advanced methods